The smart Exia exoskeleton from German Bionic is the latest development in the field of active support systems for physically demanding activities. It was designed to provide targeted relief for people performing repetitive or ergonomically difficult movements such as lifting, stabilizing, or bending. Thanks to artificial intelligence, the system responds individually to users and adapts its support in real time to the respective work situation.
Unlike passive systems, the Exia exoskeleton is active and adaptive. It recognizes patterns in movement sequences and responds to them – similar to modern assistance systems in vehicles. It is based on AI that uses real movement and usage data. This data comes from a wide variety of work areas, including logistics, production, and nursing. The system learns from this data how the human body reacts in typical work situations and can thus provide targeted relief, stabilization, or energy. The exoskeleton is now the seventh generation of back support systems developed by German Bionic. Each iteration has been further developed on the basis of field tests. The goal is a technology that does not adapt to humans, but rather allows humans to dictate the rhythm of the machine. Exia reverses this principle: the tool learns from humans.
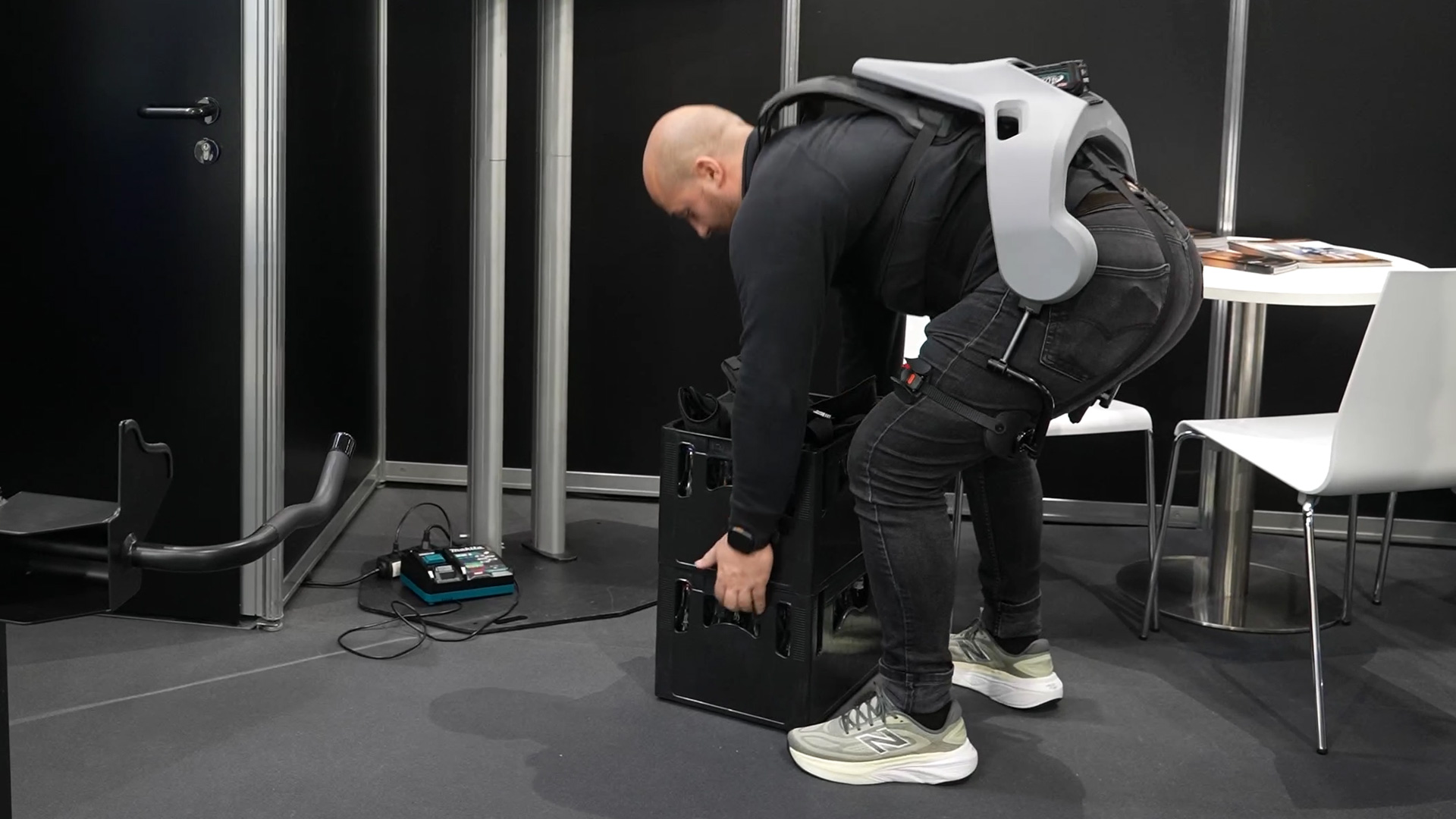

While many AI systems are trained on language, text, or images, German Bionic's augmented AI works on the basis of real movement data. It analyzes which muscle groups are used in certain activities and then calculates the optimal level of support. The result is adaptable assistance that adjusts to individual body types and work patterns within a few hours. This makes the exoskeleton not only an ergonomic aid, but also an intelligent partner in everyday work.
Exia is primarily used in logistics and healthcare. In intralogistics, it assists with material handling – for example, lifting, carrying, or stacking heavy loads. The active support reduces fatigue and ensures more precise movements, which also reduces the risk of injury in the long term.
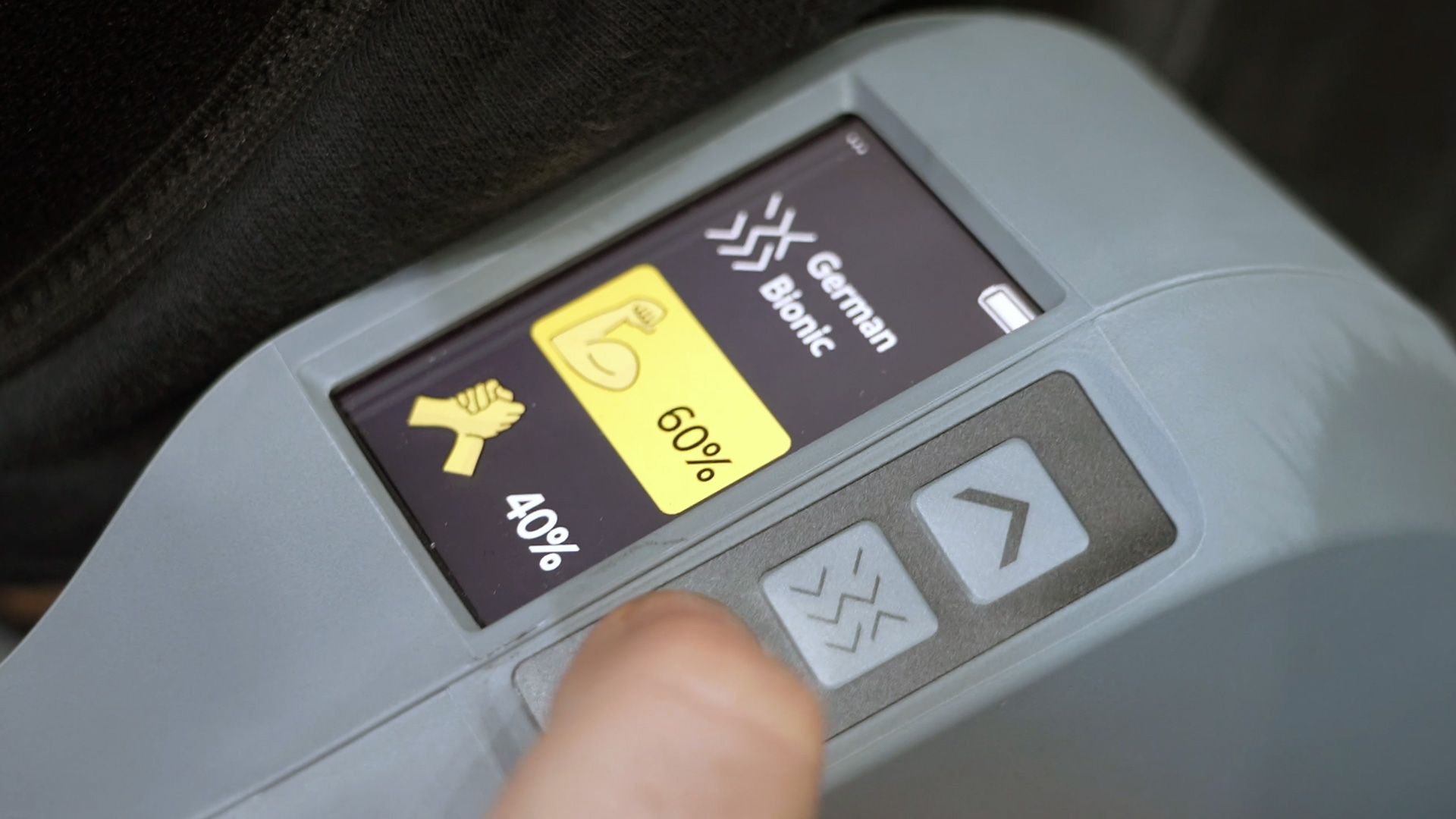


In the care sector, Exia is used in hospitals and care facilities. Here, it helps to mobilize patients or when working in bent-over positions, such as when changing bandages or performing operations. It is not a medical device, but a preventive aid for physical relief.
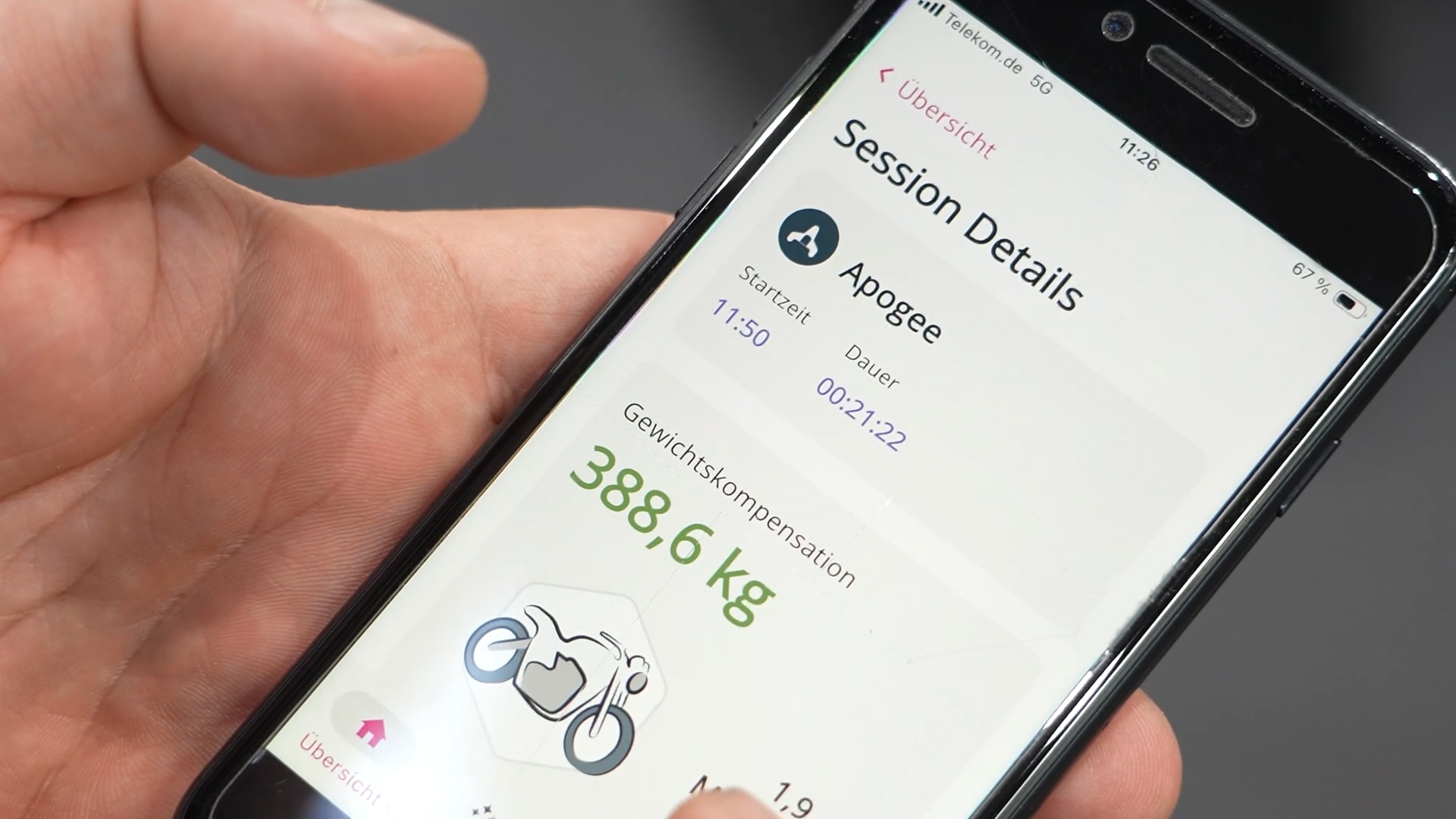
Unlike purely passive exoskeletons, Exia uses electric motors powered by batteries. The system feeds energy back into the movement in a targeted manner – a decisive advantage for repetitive physically demanding activities. This active support ensures that employees can work longer with concentration and without errors.

Less fatigue also means fewer accidents: when muscles are not overstrained, the risk of poor posture and injuries is significantly reduced. Exia thus functions not only as an ergonomic aid, but also as a preventive tool in occupational health management.